Question 9
(a) (i) Explain resonance frequency as applied in RLC series circuit.
(ii) Sketch a diagram to illustrate the variation of frequency, f, with the resistance, R, the capacitive reactance Xc, and the inductive resactnce, XL, in RLC series circuit.
(iii) Using the diagram drawn in 9(a)(ii), state whether the current in the circuit leads, lags or is in phase with the supply voltage when:
(α) f=f0;
(ꞵ) f<f0;
(γ) f>f0;
where f0 is the resonant frequency.
(b) (i) Define mutual inductance.
(ii) The coil of an electric generator has 500 turns and 8.0 cm diameter. If it rotates ina magnetic field of dendity 0.25 T, calculate the angular speed when its peak voltage is 480 V.
[π= 3.142]
(c) (i) Explain eddy currents.
(ii) State two practical uses of eddy currents
Observation
Part (ai): The question was not popular among candidates. Most candidates end up defining frequency instead of explaining. This implies that candidates did not back up their definition with additional information.
(ii) This part was fairly attempted. Candidates would have earned all the marks if they had placed fo in its proper place in the diagram.
(iii) This part was fairly attempted. Most candidates got the relationship between
current and voltage when f = fo but interchanged the solution for (ꞵ) and (γ).
Part (bi): Performance was poor. Most candidates responded wrongly to the definition of mutual inductance.
(ii)candidates were expected to recall the formula E = ωBAN and substitute to solve for ω after calculating radius from diameter of 8.00 cm and using πr2 to determine the area. Most candidates could not do this and therefore got a wrong answer.
Part (c): Performance was fair. Most candidates could not explain eddy current and also was unable to state practical uses of eddy current in 9 c(ii)
The expected answer is:
(a)(i) Explanation of resonance frequency as applied to RLC series circuit
It is the frequency of oscillation of an RLC series circuit when the capacitive reactance is equal to the inductive reactance. The impedance is equal to the resistance/the current is then maximum/the impedance is minimum.
(ii)A sketched graph to show variation of f with R, XC and XL
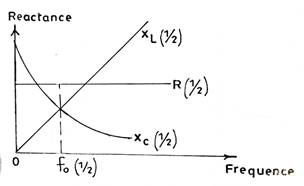
(iii)(a) Relationship between current and voltage when f = f0
Current is in phase with the supply voltage.
(b) Relationship between current and voltage when f < f0
Current lags the supply voltage.
(g) Relationship between current and voltage when f > f0
Current leads the supply voltage.
(b)(i) Definition of mutual inductance
The ratio of the induced emf in one coil/circuit to the time rate of change of current in the other coil.
OR
The production of e.m.f in a circuit as a result of the change in the magnetic flux/magnetic circuit in an adjacent circuit linked to it
(ii) Calculation of angular speed of the coil of an electric generator
E = wBAN
480 = w x 0.25 xp x ![]() x 500
x 500
w = 763.8 rad s-1
(c)(i) Explanation of eddy current
The current induced and flows within a metal block when there is a change in magnetic flux linking the block.
OR
Loops of electric current induced within a conductor by the changing magnetic flux/field in the conductor
OR
The localized electric current/loops of electric current
(ii) Practical Uses of eddy current
- induction furnaces
- induction coils
- speedometers
- induction motors
