Question 1
The equilibrium position of a firm is illustrated in the diagram below. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
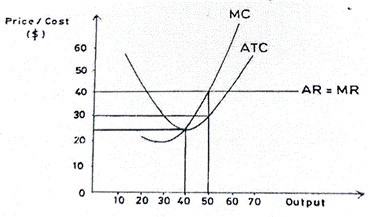
(a) Determine the firm’s:
(i) equilibrium output level;
(ii) equilibrium price.
(b) At the equilibrium output level, calculate the firm’s:
(i) total cost;
(ii) total revenue;
(iii) total profit.
(c) Is the firm operating in the long-run or short-run? Explain your answer.
(d) (i) What type of market is the firm operating in?
(ii) List three features of the market type identified in (d)(i).
The candidates were expected to provide the following answers to score higher marks.
(a) (i) Equilibrium output level = 50 units
(ii) Equilibrium price = $ 40.00
(b) (i) Total cost (TC) = AC × Q
= $ 30 × 50
= $ 1500
(ii) Total revenue (TR) = AR × Q
= $ 40 × 50
= $ 2000
(iii) Profit = TR – TC
= $ (2000 – 1500)
= $ 500
OR
Profit = (AR – AC) × Q
= $ (40 – 30) × 50
or
= $ 10 × 50
= $ 500
(c) The firm is operating in the short-run because it is operating in a perfect market and it made abnormal/super normal profit, where its price > average cost and average cost < average revenue.
(d) (i) Perfectly competitive market/perfect market.
(ii) - There are many buyers and sellers.
- There is free entry and exit into and from the market.
- Sellers are price takers/there is one market clearing price/there is no government intervention.
- There is perfect knowledge about the market.
- There are no extra transport costs incurred.
- Goods sold are homogeneous.
- There is no preferential treatment.
