Question 2
This question was popular among the candidates and their performance was above average.
- (a) (i) What ar structural isomers?
(ii) Write the structure and name of one:
I Straight chain;
II Branched chain;
III isomer of C4H9Cl. [6 marks]
(b) Explain briefly how the shapes of molecules are formed. [4 marks]
(c) Consider the following equilibrium reaction.
A(g) + 3B(g) 2C (g)ΔΘ = +ve
State and explain the effect of each of the following changes on the equilibrium position:
- increasing the pressure on the system;
- adding a catalyst to the system;
- increasing the temperature of the system.
[6 marks]
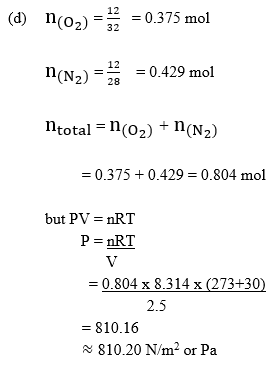
(d) Determine the total pressure exerted by a mixture of 12.0 g N2(g) and 12.0 g O2(g) in a 2.5 m3 container at 30°C.
[R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1, N2 = 28.0, O = 32.0] [9 marks]
Observation
This question was popular among the candidates and their performance was above average.
In part (a), majority of the candidates could not define structural isomers.
In part (b), majority of the candidates could not explain how the shapes of molecules are formed.
In part (c), majority of the candidates state and explain the effect of increasing the pressure on the system and addition of a catalyst to the equilibrium reaction.
In part (d), majority of the candidates could not determine the total pressure exerted by a mixture of the gases.
The expected answers include:
(a) (i) Structural isomers are two or more compounds with the same molecular formula
but different structural formulae / arrangement of atoms.
(ii) Straight Chain
H H H H
| | | |
H – C – C – C – C – CL 1 – Chlorobutane
| | | |
H H H H
OR
H H CL H
| | | |
H – C – C – C – C – H 2 – Chlorobutane
| | | |
H H H H
Branched chain
H H CL
| | |
H – C – C – C – CL 1 – Chloro-2-methylpropane
| | |
H H-C-H H
|
H
H CL H
| | |
H – C – C – C – CL 2 – Chloro-2-methylpropane
| | |
H H-C-H H
|
H
(b) Pairs of electrons around a central atom repel each other arranging themselves as far apart as possible to minimize the repulsion / have maximum stability
(c) (i) 4 moles of gaseous reactants give 2 moles of gaseous products / pressure decreases from left to right.
The system will therefore shift the equilibrium position to the right so the pressure of the system can be reduced.
(ii) Addition of a catalyst has no effect on the equilibrium position of the reactant (1). A catalyst only reduces the activation energy of the reaction (1) / affects both forward and backward reactions at the same rate
(iii) Increasing temperature will shift the equilibrium position to the right. Since the forward reaction is endothermic / H is positive (it will absorb the added heat)