This question was attempted by many candidates and their performance was fair. In part (a) candidates could not correctly draw and label the diagram as been specified in the question. In part (b) candidates could not correctly state function of the parts labelled of a typical animal cell. as seen under a light microscope. In part (c) candidates correctly stated methods by which the spread of malaria can be controlled. In part (d) candidates wrongly wrote methods of refuse disposal as methods of preventing water pollution.
However, the expected answers were as follows:
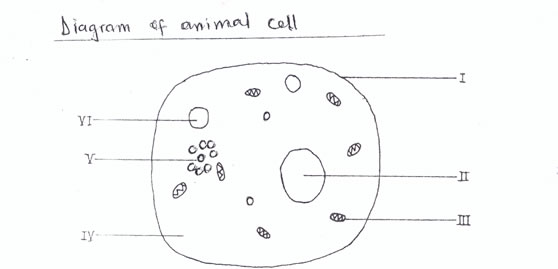
Accuracy
NB: Nucleus should be indicated. Cell should be roughly circular
Dimension – not less than 10 lines
I - cell membrane VI - cytoplasm
II - nucleus V - glycogen granule
III - mitochondrion VI - vacuole
(b) Function of the labelled parts
Function Nucleus
- controls activities of cell
- it allows exchange of materials between the nucleus and cytoplasm
- development of genetically acquired traits/hereditary materials
Function Vacuole
- It acts as a store house for excretory products
Function mitochondrion
- for respiration
- it acts as power house (for energy)
Function glycogen granule
- stores animal starch/glycogen
Function cell membrane
- it prevents the cell contents from escaping
- it controls the materials which are allowed to enter or leave the cell.
(c) Methods of Controlling malaria
- use drugs to destroy parasite in humans
- destruction of larvae pouring oil on stagnant water
- destruction of adult mosquitoes using insecticide
- live in mosquito proof houses
- introduce fish into water to feed on larvae
- destruction of bleeding places
- destruction of hiding places
- education/public awareness
(d) Methods of preventing water pollution
- legislation
- treatment of raw sewage before discharge into water/proper disposal of
sewage
- recycling of industrial waste
- educate farmers on the correct usage of fertilizers to limit run-off into water bodies
- ban the use of chemical in fishing
- waste must be discharged in controlled amount
- oil leakages must be prevented from tankers
- use of organic manure other than fertilizers to be encourage
- avoid thermal pollution/coding of liquid wastes from factories.
|



